If you live in the mountains, you’re probably aware of the unique hazards associated with this environment. You may get something out of this week’s article but it is meant for people that are either city dwellers or live down in the flat. It will be a big help to the people of California that are trying to escape over the mountains before Governor Moonbeam builds his wall. Seriously though, the effects of altitude on the body, environment and weather make mountain survival truly unique.
the mountains before Governor Moonbeam builds his wall. Seriously though, the effects of altitude on the body, environment and weather make mountain survival truly unique.
If you find yourself having to cross large mountain ranges, stick to the passes or canyons. Figuring that it would be shorter to go over the mountain, rather than around it may be true for birds but unless you’re in an airplane, it’s not so for humans. They may not look steep from a distance and even as you begin scaling them they may not seem bad, until they are. Nonacclimatized individuals rapidly ascending above 3,000 meters (9800 feet) are at risk of developing high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE), a life threatening condition where the air pockets in the lungs fill with liquid.
Nonacclimatized individuals rapidly ascending above 3,000 meters (9800 feet) are at risk of developing high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE), a life threatening condition where the air pockets in the lungs fill with liquid.
Many people are afraid of bears or mountain lions or wolves or some such animal, that they are going to be attacked or eaten, but you are far more likely to die from the elements. The mountain will kill you before something that lives on the mountain will.
I will include a quick note about wild animals… For the most part they are more afraid of you than you are of them. There are very few actual man eaters in the mountains. Even grizzly bears and mountain lions would much prefer easier prey than humans. That said there’s no sense tempting fate, so when encountered give them a wide berth, but DO NOT run from them. This same advice should include ANY large animals that have young with them. You seriously don’t want to get between momma and her baby! Your food can attract animals, especially meat, so take care to keep any that you may be carrying in airtight wrapping.
Even grizzly bears and mountain lions would much prefer easier prey than humans. That said there’s no sense tempting fate, so when encountered give them a wide berth, but DO NOT run from them. This same advice should include ANY large animals that have young with them. You seriously don’t want to get between momma and her baby! Your food can attract animals, especially meat, so take care to keep any that you may be carrying in airtight wrapping.
Temperature can be a killer on the mountain. During the spring and fall, the daytime temperature can be, depending on altitude, up in the 70’s or 80’s (Fahrenheit) but at night can still get down below freezing. So it’s very important to layer your clothes! If you’ve been out hiking all day and your clothes are sweaty and wet, and then the temperature drops off fast at night you could find yourself in a hypothermia situation.
Weather at high altitude can change rapidly, due in part to the more powerful and steady winds aloft. Also as water vapor forms clouds and is blown across the mountains, even if it doesn’t become a storm, due to the resulting contact with the ground, water condenses on objects making you and your gear wet. As I talk about in The Rule of 3’s, one of the first things you should think about, especially in a mountain environment is protection from the elements. Starting with your clothes, you should have at least 2 ways to stay dry, and a method of building and/or maintaining a shelter.
due to the resulting contact with the ground, water condenses on objects making you and your gear wet. As I talk about in The Rule of 3’s, one of the first things you should think about, especially in a mountain environment is protection from the elements. Starting with your clothes, you should have at least 2 ways to stay dry, and a method of building and/or maintaining a shelter.
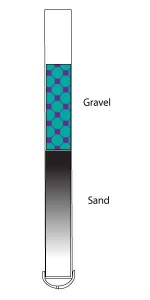
Another concern is the need for water. The air at high altitude is very dry (when there’s no precipitation present) especially in the winter when the moisture in the air is frozen. This leads to… DON’T EAT THE SNOW! Although it satisfies the need for water, it erodes the need for shelter; in that it lowers the core body temperature and can lead to hypothermia. There is a long running myth that fast moving water is safe to drink, all ground water found in nature should be treated or filtered before consumption. There is the possibility that you will be okay drinking it, however any bacteria present could result in stomach cramps, diarrhea, even parasites. I don’t think I need to tell you that if you’re running from Governor Moonbeam’s stormtroopers, drinking bad water will really slow you down!
need for water, it erodes the need for shelter; in that it lowers the core body temperature and can lead to hypothermia. There is a long running myth that fast moving water is safe to drink, all ground water found in nature should be treated or filtered before consumption. There is the possibility that you will be okay drinking it, however any bacteria present could result in stomach cramps, diarrhea, even parasites. I don’t think I need to tell you that if you’re running from Governor Moonbeam’s stormtroopers, drinking bad water will really slow you down!